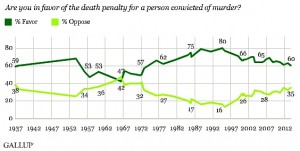
Sixty percent of Americans say they favor the death penalty for convicted murderers, the lowest level of support Gallup has measured since November 1972, when 57% were in favor. Death penalty support peaked at 80% in 1994, but it has gradually declined since then.
Gallup first asked Americans their views on the death penalty using this question in 1936, and has updated it periodically since then, including annual updates since 1999.
Americans have typically favored the death penalty; in fact, support has exceeded opposition in all but one survey, conducted in May 1966, during an era marked by philosophical and legal challenges to the death penalty from the mid-1950s through the early 1970s. Americans’ support for the death penalty waned during that time. The culmination of that era was the Supreme Court’s 1972 Furman v. Georgia decision, which invalidated all state death penalty statutes on technical grounds but stopped short of declaring the practice itself unconstitutional. Four years later, the court ruled that several newly written death penalty laws were constitutional, and executions resumed in the U.S. shortly thereafter.